
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Window Energy Ratings, What They Mean, And What You Should Do About It
In the upper left-hand corner of the window will be a label describing its energy rating. Said rating comes from the National Fenestration Ratings Council (NFRC). There are specific standards that define certain window quality thresholds. We’ll expand on those standards here. They include:
• The U-Factor
• Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
• Visible Transmittance
• Air Leakage
• Condensation Resistance
The U-Factor
The U-Factor pertains to heat retention–or, rather, loss. When it comes to the U-Factor, the lower the number, the better the insulation. U-Factor numbers will typically be somewhere between .2 and 1.2. It’s a lot like “R-Value” in terms of overall insulation, only with R-value, the higher the number, the greater the insulation.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
When you’re thinking about solar heat gain, the term “coefficient” refers to how this is mathematically rendered. The abbreviation for this mathematical rendering is SHGC. The associated number demonstrates a given product’s ability to keep out solar heat. This number will be represented between 0 and 1. The lower the number, the better in terms of solar heat gain reduction for the U-Factor.
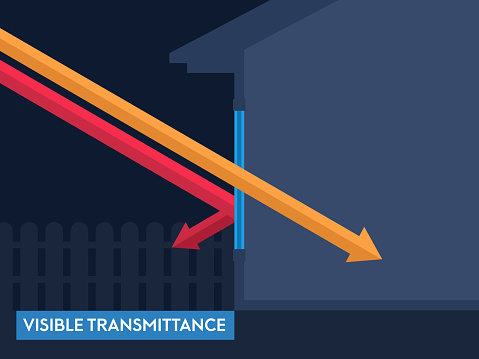
Visible Transmittance
Also expressed in a number between 0 and 1 is a quality called Visible Transmittance, or VT. More light is transmitted if the number is higher, less if the number is lower.
Air Leakage
Air Leakage, AL, is calculated by averaging expected air loss in cubic feet per square feet, defining a window’s surface. Air will come through cracks in the window. You’re looking for a low number in AL, as it will indicate fewer cubic feet of air coming through window cracks. The larger the window, the higher the AL, so you’re looking to determine square feet proportions.

Condensation Resistance
Condensation Resistance is CR and is a measure of a window’s strength in terms of resistance condensation. You’re looking for a high number here. The greater the CR rating, the more resistance to condensation a window will have.
Making Window Decisions Based Around NFRC Ratings Solidifies Your Purchase
With SHGC, you’re looking for a lower number, and the same is valid for the U-Factor. You’re looking for a high CR rating and a low AL rating. VT ratings may be higher or lower; it depends on how much light you want coming in.
Semper Fi Exteriors can be a great resource regarding window design and associated NFRC ratings. Understanding this information helps you assure you make the best purchase decisions as regards windows. Get in touch with us to learn more.



